Table of Contents
INSTRUCTION SET
An instruction set can be defined as a group of instruction that a processor can execute to perform different operations. The instruction is defined as a machine language command to perform a specific task. Each instruction has two parts
- Opcode
- Operand
Opcode means Operation + Code
It specified the operation to be performed by their instruction
Example:-ADD, MOV, MVI
Operand:- It specifies the memory location where the input and output data are kept.
# On The Basis Of Complexity the InstructionSet Can Be Classified As:-
- CISC (Complex Instruction set Computer)
RISC(Reduced Instruction set Computer)
CISC | RISC |
1. Very complex and large no. of instruction. | 1. Simple and less no. of instruction |
2. Number of instruction is about 100-250 | 2. Number of instruction is about 0-100 |
3. Longer time of execution | 3. Less time of execution |
4. Slow Speed | 4. High speed |
5. Memory based instruction | 5. Register based instruction |
6. Complex Design | 6. Simple and easy Design |
7. Solve complex task in the complex way | 7. Solve complex task in the simple way |
# According to the number of bytes there are three categories of instruction
- One byte instruction
- Two byte instruction
Three byte instruction
One byte instruction:- One byte for execution.
Two byte instruction:- One byte for execution, One byte for operand.
Three byte instruction:- One byte for execution, Two byte for operand.
BUS ARCHITECTURE
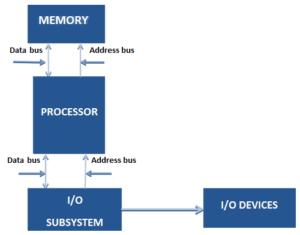
A bus is a set of wire that is used to connect the different internal components of a computer system for transferring data, address and control.
There may be several buses in a computer system
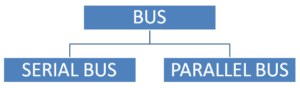
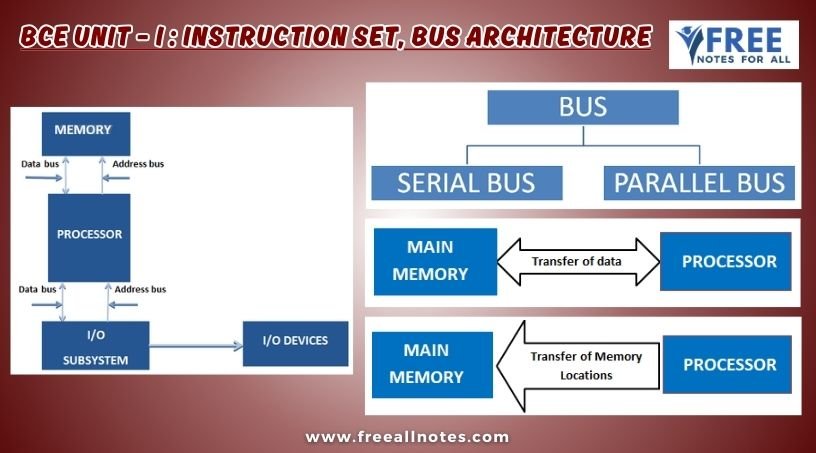
The speed of any type of bus is measured in terms of the number of bits transferred per second, between two components.
In Serial Bus only one bit of data is transferred at a time, amongst the various hardware components.
In Parallel Bus, several bits of data can be transferred at a time, amongst the various hardware components.
The figure depicts the two different types of buses according to the type of operations performed by them. These buses are data bus and the address bus, a third type of bus known as control bus- also exists in a computer system.
The Control Bus manages the transfer of data and address among various components by transferring appropriate control signals.
# DATA BUS
The Data bus in a computer system is used to transfer data amongst the different internal components. The speed of the data bus also affects the overall processing power of a computer system. Modern computer system use 32-bit data buses for data transfer. This means that these buses are capable of transferring 32 bits of data at a time.

The data bus implemented between the main memory and the processor of a computer system.
The figure shows that a bidirectional data bus is implemented between the main memory and processor of the computer system. The bidirectional data bus allows the transfer of data in both the directions. The data bus is generally bidirectional in nature in most computer system.
# ADDRESS BUS
The address bus is also known as memory bus. It transfers the memory address for read and writes memory operations. It contains a number of address lines that determine the range of memory addresses that can be referenced using the address bus.
For Example:-a 32-bit address bus can be used to reference 2 Memory locations. Like data bus, the address bus can also be a serial or a parallel bus.

Figure shows the address bus used for transferring memory locations between processor and memory. The address bus between the main memory and processor of a computer system is unidirectional. However, an address bus also is bidirectional. For example, the address bus between the processor and the I/O system is bidirectional.
Add Your Heading Text Here
You May Like to Browers More